Why Two-Factor Authentication is Important
How Does Multi-Factor Authentication Work?
Key Takeaways:
- Adding to the arsenal of threats is the emergence of AI-driven attacks.
- MFA blocks a whopping 99.9% of modern automated cyberattacks.
- The cost of implementing a strong MFA practice is negligible compared to the recovery time from a cyberattack.
Over the last few years, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) has become a critical technology. IT professionals have been encouraging its adoption, and it has become essential for obtaining insurance and meeting compliance requirements for Cyber Liability Applications.
A cautionary tale – UnitedHealth Group reported a loss of $870 million due to a cyberattack in early 2024. The focus was on the lack of MFA in their cybersecurity practices, which may have left the system vulnerable to such attacks.
What’s Multi-Factor Authentication?
MFA is a security authentication practice requiring users to prove their identity through two sources. For example, after entering your username and password to access your email, you must enter a time-sensitive code sent to your smartphone. Cybercriminals might easily steal your username and password, but they will have a harder time stealing the code from your phone before it expires.
The most popular MFA methods for this second layer of security are:
- Things you know – a PIN number
- Things you have – security badge or smartphone
- Things you are – your fingerprint or through voice recognition
The cost of implementing a strong MFA practice is negligible compared to the recovery time from a cyberattack. However, plenty of organizations are still not using it. Threat actors and cybercriminals know this and focus their efforts on this low-hanging fruit.
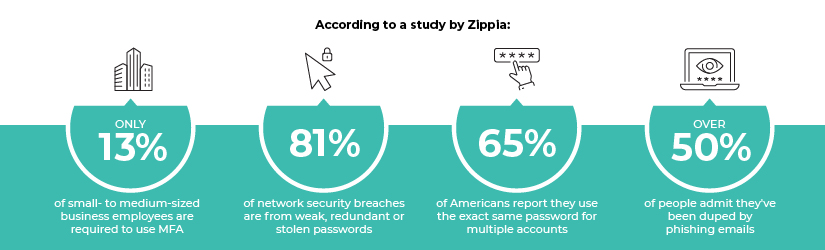
What are the Benefits of Multi-Factor Authentication?
- Increased Security: Requiring users to provide additional proof of identification before access is granted makes it much more challenging for the hacker to succeed. Even if they manage to steal one factor, like the user’s password, they still need the additional factor to gain access.
- Protection Against Phishing: It mitigates the risk of phishing email attacks, where attackers trick users into divulging their usernames and passwords. With MFA in place, the attacker would still be unable to access the account without the second factor.
- Compliance Requirements: Many regulatory standards, such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), require MFA as part of an organization’s security practices.
- Adaptive Authentication: Advanced MFA systems use adaptive authentication, which adjusts the authentication requirements based on factors like the user’s location or the type of device they are using.
Companies that do not enforce MFA expose themselves to many risks.
Human error or relaxed authentication practices enable attackers to gain access through tactics like phishing or brute force attacks. The repercussions of these breaches can yield huge financial losses, legal liabilities, regulatory fines and irreparable damage to a company’s reputation.
Adding to the arsenal of threats is the emergence of AI-driven attacks. Cybercriminals use sophisticated algorithms to automate and optimize their strategies. As AI capabilities continue to evolve, companies without MFA face a considerable risk.
Does Multi-Factor Authentication Work?
MFA blocks a whopping 99.9% of modern automated cyberattacks.
Adopting and implementing MFA is a fundamental pillar of cybersecurity defense. It provides simple yet effective protections for both the individual user and the entire company. Instead of asking yourself why you need to implement MFA, it’s time to ask yourself why you haven’t already done it. Contact an Adams Brown technology advisor to learn more about implementing MFA for your business.

